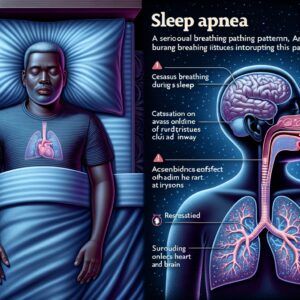
Sleep apnea is a potentially serious sleep disorder characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep, which can significantly impact your overall health and quality of life. While many people may dismiss it as simply loud snoring or mild discomfort, untreated sleep apnea poses hidden dangers that extend far beyond disrupted rest.
Chronic oxygen deprivation resulting from these frequent pauses in breathing places immense strain on vital organs such as the heart and brain, increasing the risk for severe medical conditions, including hypertension, stroke, diabetes, and even sudden cardiac death. Understanding how this condition affects your body over time—and recognizing when it becomes life-threatening—is crucial to safeguarding your health.

Your future is calling! Answer at Great Life Worldwide and discover why it’s the perfect fit for you. Free tour available – act fast!
1. What Exactly is Sleep Apnea and Why Should You Be Concerned?
Sleep apnea is a severe sleep disorder characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep, resulting from either partial or complete obstruction of the airway. These pauses in breathing can last anywhere from a few seconds to over a minute and may occur dozens or even hundreds of times throughout the night. There are primarily three types of sleep apnea: obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), central sleep apnea (CSA), and complex or mixed sleep apnea, which combines elements of both OSA and CSA.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea, the most common form, occurs when throat muscles relax excessively during sleep, causing soft tissues at the back of your throat to collapse inwardly and block airflow. Central Sleep Apnea differs significantly as it involves dysfunction within the brain’s respiratory control center; here, signals that regulate breathing fail to transmit properly between your brain and respiratory muscles.
The reason you should be concerned about this condition lies not only in its immediate effects—such as daytime fatigue, impaired cognitive function, irritability—but also because untreated sleep apnea has been linked directly with severe long-term health consequences. Chronic oxygen deprivation due to interrupted breathing episodes places significant stress on vital organs like your heart and brain.
Over time, this increases risks for hypertension (high blood pressure), stroke events including transient ischemic attacks (“mini-strokes”), type 2 diabetes mellitus development or worsening symptoms thereof if already present, and even sudden cardiac death under certain circumstances.
Feel Better, Live Better, Earn More—Only with GreatLife.
2. How Does Sleep Apnea Affect Your Body Over Time?
Sleep apnea, when left untreated, can significantly impact various systems within your body over an extended period. One of the primary consequences is cardiovascular strain; repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep cause oxygen levels to drop abruptly, placing considerable stress on the heart and blood vessels. This chronic stress contributes to hypertension (high blood pressure), arrhythmias (irregular heartbeat), and increases the risk of developing coronary artery disease or experiencing a stroke.
Additionally, untreated sleep apnea hurts metabolic health by disrupting insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. Individuals with prolonged sleep apnea are more susceptible to type 2 diabetes due to impaired glucose regulation caused by intermittent hypoxia—periods of reduced oxygen supply—and fragmented sleep patterns that disrupt hormonal balance.
The respiratory system also suffers from ongoing disturbances associated with obstructive episodes characteristic of this condition. Chronic inflammation resulting from frequent airway obstruction may exacerbate existing respiratory conditions such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Furthermore, persistent fatigue resulting from poor-quality rest affects cognitive functions, including memory retention, concentration, decision-making skills, and overall mental clarity.
Finally, long-term effects extend into emotional well-being; individuals frequently experience mood disorders like depression or anxiety stemming directly from inadequate restorative sleep cycles combined with physiological stresses imposed upon their bodies nightly. Consequently, addressing symptoms early through proper diagnosis and treatment becomes crucial for preventing the cumulative detrimental effects on one’s physical health and psychological well-being over time.
Craving success? Satisfy your ambition at Great Life Worldwide. Learn about the incredible opportunities and take a free tour now. Don’t delay!
3. Could Sleep Apnea Lead to Death? The Risks Explained
Sleep apnea, when left untreated, can indeed pose serious health risks that may ultimately lead to death. Although the condition itself rarely causes immediate fatality, its long-term consequences significantly increase the likelihood of life-threatening complications. One of the most critical dangers associated with sleep apnea is cardiovascular disease.
Repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep cause oxygen levels in the blood to drop sharply, placing considerable strain on the heart and circulatory system. Over time, this stress elevates blood pressure and increases susceptibility to conditions such as hypertension, stroke, heart attacks, and arrhythmias—all potentially deadly if not properly managed.
Additionally, untreated sleep apnea heightens the risk of developing type 2 diabetes due to disruptions in insulin regulation caused by chronic poor-quality sleep and intermittent hypoxia (low oxygen). Diabetes further compounds cardiovascular risks and contributes directly or indirectly to mortality rates among affected individuals.
Another significant danger arises from daytime fatigue resulting from disrupted nighttime rest. Individuals suffering from severe, untreated sleep apnea often experience excessive daytime drowsiness that impairs cognitive function and reaction times. This impairment dramatically increases their chances of involvement in motor vehicle accidents or workplace injuries, both scenarios capable of causing sudden death or severe injury.
Finally, prolonged exposure to low oxygen levels at night has been linked with increased inflammation throughout the body, a factor known for contributing substantially towards various chronic illnesses, including cancer progression and respiratory failure.
Therefore, while it may seem unlikely initially that a sleeping disorder could be fatal in and of itself, understanding these indirect yet substantial threats underscores the crucial importance of timely diagnosis and treatment in preserving one’s overall health—and even life itself—in cases involving obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS).
4. When Does Sleep Apnea Become Life-Threatening?
Sleep apnea becomes life-threatening when it significantly disrupts breathing patterns, leading to prolonged oxygen deprivation and severe cardiovascular complications. Individuals experiencing frequent episodes of interrupted breathing during sleep may suffer from chronic hypoxia—an inadequate supply of oxygen reaching the body’s tissues, which places immense strain on vital organs such as the heart and brain. Over time, this persistent lack of oxygen can trigger severe health conditions, including hypertension, stroke, arrhythmias, and even heart failure.
Additionally, untreated obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) substantially increases the risk for sudden cardiac death due to its direct impact on cardiovascular function. During apneic events, blood pressure surges dramatically as the body attempts to restore standard breathing patterns; these repeated fluctuations can damage arterial walls and contribute to plaque buildup in arteries, a precursor to potentially fatal cardiac incidents.
Moreover, severe cases of sleep apnea significantly increase daytime fatigue levels, impairing cognitive functions such as concentration and reaction times. This impairment significantly elevates accident risks while driving or operating machinery—situations that could quickly become deadly not only for individuals with untreated OSA but also for others around them.
Ultimately, recognizing when sleep apnea crosses into dangerous territory involves closely monitoring symptom severity: frequent choking sensations at night, accompanied by pronounced daytime exhaustion, warrant an immediate medical evaluation. Early intervention through proper diagnosis followed by appropriate treatment measures is essential in preventing life-threatening outcomes associated with advanced stages of untreated sleep apnea.

Take Control of Your Wellness and Wealth—Start Your GreatLife Today.
5. Common Misconceptions: Can Sleep Apnea Kill You?
A common misconception surrounding sleep apnea is that it merely causes loud snoring or mild discomfort during sleep, leading many to underestimate its potential severity. In reality, untreated sleep apnea poses significant health risks and can indeed be life-threatening if left unmanaged.
One prevalent myth is the belief that because individuals with sleep apnea eventually wake up gasping for air, they are not truly at risk of suffocation or death during their sleep. However, this repeated interruption in breathing significantly stresses the cardiovascular system over time.
Another widespread misunderstanding is that only severely overweight or elderly individuals face serious consequences from sleep apnea. While obesity and age are known risk factors, younger adults and those within a healthy weight range can also suffer from severe forms of this condition. Ignoring symptoms based on these misconceptions delays diagnosis and treatment, increasing vulnerability to complications such as hypertension, stroke, heart attack, diabetes mellitus type 2, and even sudden cardiac death.
Furthermore, some people mistakenly assume that daytime fatigue caused by disrupted nighttime breathing is simply an inconvenience rather than a potentially dangerous symptom indicative of underlying systemic damage. Chronic exhaustion resulting from untreated sleep apnea increases accident risks, particularly motor vehicle accidents, and negatively impacts cognitive function and mental health.
Dispelling these myths requires education about the true nature of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) as a chronic medical condition demanding professional evaluation and intervention. Recognizing its seriousness helps patients seek timely care before irreversible harm occurs or fatal outcomes become imminent realities rather than distant possibilities.
Ready to soar? Take flight with Great Life Worldwide! Learn why it’s your launchpad to success. Free tour available – act now!
6. Warning Signs That Your Sleep Apnea May Be Putting Your Life at Risk
Recognizing the critical warning signs of severe sleep apnea is essential to preventing potentially life-threatening complications. One primary indicator that your condition may be worsening dangerously is excessive daytime fatigue, which goes beyond typical tiredness and significantly interferes with daily activities, such as driving or working safely. If you find yourself frequently dozing off unintentionally during routine tasks, this could signal inadequate oxygenation due to repeated breathing interruptions at night.
Another concerning symptom is loud and persistent snoring accompanied by choking or gasping sounds during sleep. These episodes indicate airway obstruction severe enough to momentarily halt breathing, placing substantial stress on your cardiovascular system and increasing the risk of hypertension, heart attacks, or strokes over time.
Morning headaches are also a red flag; they often result from reduced oxygen levels overnight caused by frequent apneic events. Additionally, waking up feeling short of breath or experiencing chest discomfort can suggest underlying cardiac strain related directly to untreated sleep apnea.
Mood changes such as irritability, depression, anxiety, or difficulty concentrating should not be overlooked either. These psychological symptoms can reflect chronic sleep deprivation linked closely with untreated obstructive episodes occurring nightly.
Lastly, if you have been diagnosed previously but notice an escalation in these symptoms despite treatment efforts, or if family members express concern about witnessing prolonged pauses in your breathing while asleep, you must seek immediate medical evaluation. Prompt attention ensures timely intervention before serious health consequences arise from advanced stages of untreated sleep apnea.
7. Protecting Yourself: Effective Ways to Manage and Treat Sleep Apnea
Effectively managing sleep apnea is crucial for safeguarding your health and reducing the risk of serious complications. One of the most commonly recommended treatments by healthcare professionals is Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy, which involves wearing a mask connected to a machine that delivers consistent airflow, thereby keeping airways open during sleep. CPAP has proven highly effective in alleviating symptoms, improving sleep quality, and significantly decreasing cardiovascular risks associated with untreated sleep apnea.
In addition to CPAP therapy, lifestyle modifications can substantially improve outcomes for individuals suffering from this condition. Weight loss through diet and regular exercise can reduce excess tissue around the airway, thereby minimizing obstruction during sleep. Avoiding alcohol consumption before bedtime and quitting smoking are also beneficial strategies since both substances contribute to airway inflammation and relaxation of throat muscles.
For some patients who find CPAP challenging or uncomfortable, alternative treatment options may be considered under medical supervision. Oral appliances designed by dental specialists help reposition the jaw or tongue forward during sleep to maintain an open airway effectively. Surgical interventions might also be appropriate in certain cases where anatomical abnormalities significantly obstruct breathing passages.
Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers specializing in sleep disorders ensure ongoing monitoring of treatment effectiveness and timely adjustments as needed. Adhering strictly to prescribed therapies combined with proactive lifestyle changes provides optimal protection against potential life-threatening consequences linked directly or indirectly with untreated sleep apnea.
Your Path to Financial Freedom and Health Starts Here—Join Us.
Conclusion:
Sleep apnea is more than just an inconvenience; it’s a serious medical condition with potentially fatal consequences if left untreated. Recognizing its warning signs early, such as excessive daytime fatigue, persistent snoring accompanied by choking episodes at night, morning headaches, or mood changes, can be lifesaving.
Fortunately, effective treatments like CPAP therapy combined with lifestyle modifications offer powerful tools to manage symptoms and reduce associated risks significantly. By dispelling common misconceptions about the severity of sleep apnea and proactively seeking professional evaluation and treatment options tailored specifically to individual needs, you can protect yourself from its hidden dangers and maintain optimal long-term health outcomes.